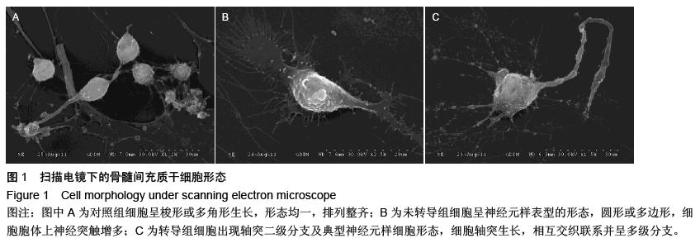
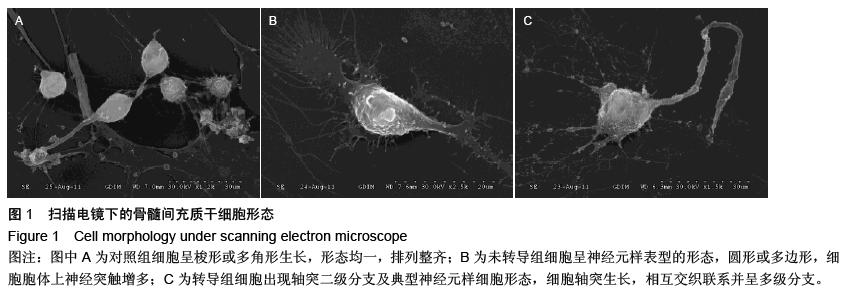
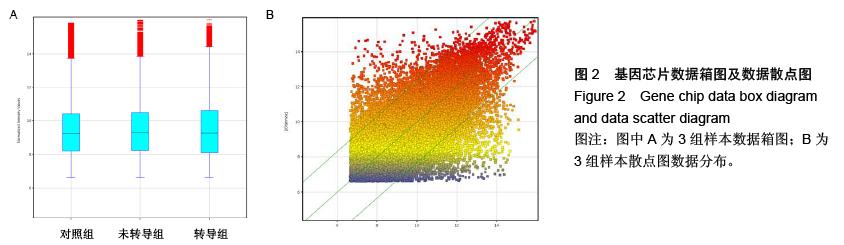
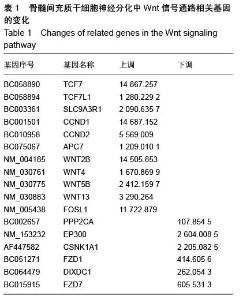
| [1] Ohishi M, Schipani E. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(2):277-282.[2] André E, Resnier P, Sindji L,et al. Neuronal programming of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 2014; 16(4):S63.[3] Guo W, Flanagan J, Jasuja R, et al. The effects of myostatin on adipogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells are mediated through cross-communication between Smad3 and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(14):9136-9145.[4] Gregory CA, Gunn WG, Reyes E, et al. How Wnt signaling affects bone repair by mesenchymal stem cells from the bone marrow. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005; 1049:97-106.[5] 李丽艳,黄金中,杜江.转化生长因子β1诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(1): 38-41.[6] Kishk NA, Gabr H, Hamdy S, et al. Case control series of intrathecal autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell therapy for chronic spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2010;24(8): 702-708.[7] Jones E, McGonagle D. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vivo. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008;47(2):126-131.[8] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[9] 赵春华.干细胞原理、技术与临床[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2006:11-14.[10] Prockop DJ, Azizi SA, Colter D, et al. Potential use of stem cells from bone marrow to repair the extracellular matrix and the central nervous system. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000;28(4):341-345.[11] Woodbury D, Schwarz EJ, Prockop DJ, et al. Adult rat and human bone marrow stromal cells differentiate into neurons. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(4):364-370.[12] 项鹏,夏文杰,李树浓.丹参注射液诱导间质干细胞分化成神经元样细胞的研究[J].中山医科大学学报, 2001, 22(5): 321-324.[13] 李浩威,肖庆忠. 麝香多肽体外诱导成年大鼠和人骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化为神经元的研究[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2002,18(10): 1179-1182.[14] Tang K, Yang J, Gao X, et al. Wnt-1 promotes neuronal differentiation and inhibits gliogenesis in P19 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293(1):167-173.[15] 阎文柱,秦书俭,刘学政,等. 体外培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(14):2476-2480.[16] Miller JR.The Wnts.Genome Biol. 2002;3(1): REVIEWS3001.[17] Nusse R, Brown A, Papkoff J, et al. A new nomenclature for int-1 and related genes: the Wnt gene family. Cell. 1991;64(2):231.[18] Cadigan KM, Nusse R.Wnt signaling: a common theme in animal development. enes Dev. 1997;11(24): 3286-3305.[19] 林治平,曾荣,胡资兵,等.Wnt信号通路与骨髓间充质干细胞神经分化[J].广东医学,2011, 4(8):1077-1079.[20] Marshall A, Hodgson J. DNA chips: an array of possibilities. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16(1):27-31.[21] 曾荣,林治平,胡资兵,等.骨髓间充质干细胞神经分化中Wnt信号通路的基因芯片分析[J].广东医学,2012, 20(8): 3031-3015. [22] Bodine PV.Wnt signaling control of bone cell apoptosis. Cell Res. 2008;18(2):248-253.[23] Liu T, DeCostanzo AJ, Liu X, et al. G protein signaling from activated rat frizzled-1 to the beta-catenin-Lef-Tcf pathway. Science. 2001;292(5522):1718-1722.[24] Polakis P.The adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta. 1997; 1332(3):F127-F147.[25] Takemaru KI, Moon RT. The transcriptional coactivator CBP interacts with beta-catenin to activate gene expression. J Cell Biol. 2000;149(2):249-254.[26] Etheridge SL, Spencer GJ, Heath DJ, et al. Expression profiling and functional analysis of wnt signaling mechanisms in mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2004;22(5):849-860.[27] Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, et al. LDL-receptor- related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature. 2000;407(6803):530-535.[28] Wang S, Krinks M, Lin K, et al. Frzb, a secreted protein expressed in the Spemann organizer, binds and inhibits Wnt-8. Cell. 1997;88(6):757-766.[29] Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell. 2005;8(5): 739-750.[30] Gao K, Wang YS, Yuan YJ, et al.Neuroprotective effect of rapamycin on spinal cord injury via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(6): 951-957[31] De Boer J, Wang HJ, Van Blitterswijk C. Effects of Wnt signaling on proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(3-4): 393-401.[32] Zhang X, Podsypanina K, Huang S, et al. Estrogen receptor positivity in mammary tumors of Wnt-1 transgenic mice is influenced by collaborating oncogenic mutations.Oncogene. 2005;24(26): 4220-4231. |